RFID technology ensures the safety of blood in the blood bank
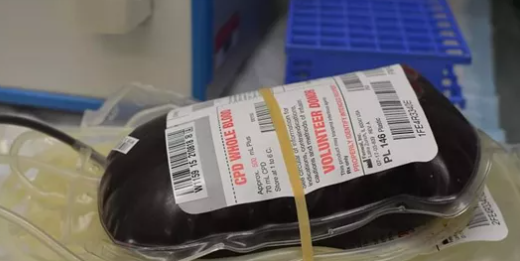
According to news from Chennai, the capital of Tamil Nadu, India, in order to better monitor and strengthen the supply chain management of blood and blood products, RFID will be introduced on a pilot basis in the blood banks of two major hospitals in the country.
When Minister Subramanian, Chief Economic Adviser of India, spoke at the state assembly, he passed the request for funding to the health sector. He said that the system will be deployed at Rajiv Gandhi Government General Hospital (RGGGH) in Chennai and Madurai. The Rajaji Medical College Hospital was established at a cost of 20.8 million rupees.
According to doctors, the system will mainly help monitor the temperature in the freezer that stores blood and blood components. "The RFID system will issue an alarm to warn of any temperature deviation." said Dr. Subashi, the RFID technology implementation liaison officer and head of the RGGGH blood bank department.
The RFID system uses radio frequency waves as its working principle and has two components: a reader and a tag. The doctor explained that the RFID reader will be connected to the computer, and the RFID tag will be connected to the blood bag with a barcode. The RFID tag will also store detailed information such as expiration date, storage date, and shelf life.
"RFID not only helps to monitor the inventory of blood banks, but also helps to track blood bags more easily. Many times before, whether the blood bags are still in inventory or whether they have been transferred is not clear to us. With RFID, This will greatly reduce the workload of the staff. If the technology is successfully implemented, it will also be extended to other government blood banks." Subashi said.
Since there have been several complaints about improper maintenance of the freezer storing screened and unscreened blood in the past, it can be said that the implementation of the RFID system is now welcomed and recognized by the public. It is worth noting that in 2019, the Ministry of Health issued an order to take action against blood bank medical staff, nurses and laboratory technicians at Hosur Medical College and Krishnaji Government Hospital in Tamil Nadu. Nine parturients may die from a blood transfusion reaction. Allegedly, its refrigeration system is not properly maintained, and the women are provided with blood that is not suitable for blood transfusion.